When you digitally sign your standalone workbook EXE file, you assure end-users that the file is authentic and has not been tampered with. This process, also known as code signing, uses Microsoft Authenticode® technology to verify that the code originates from a trusted publisher.
XLS Padlock simplifies the code signing process by handling the necessary steps internally.
Why Code Signing is Important
If you plan to distribute your applications over the Internet, code signing is strongly recommended. It helps prevent web browsers and Windows from displaying “Unidentified Publisher” warnings and can also reduce the likelihood of false positives from antivirus software.

How to Obtain a Code Signing Certificate #
To sign your application, you need a valid Code Signing Certificate from a trusted Certificate Authority (CA) like Sectigo or Digicert. Other certificate types, like SSL/TLS, are not compatible.
Cloud-Based Certificates
An increasingly popular and cost-effective alternative is Azure Trusted Signing, a cloud-based service from Microsoft. It eliminates the need for physical USB tokens and streamlines the management process. XLS Padlock fully supports signing with Azure Trusted Signing.
Token-Based Certificates (HSMs) #
As of June 1, 2023, all new code signing certificate private keys must be stored on secure hardware, such as a FIPS 140-2 Level 2 compliant USB token or Hardware Security Module (HSM). This enhances security by preventing key theft. XLS Padlock works seamlessly with token-based certificates; just ensure the token is plugged into your computer when you build your application.
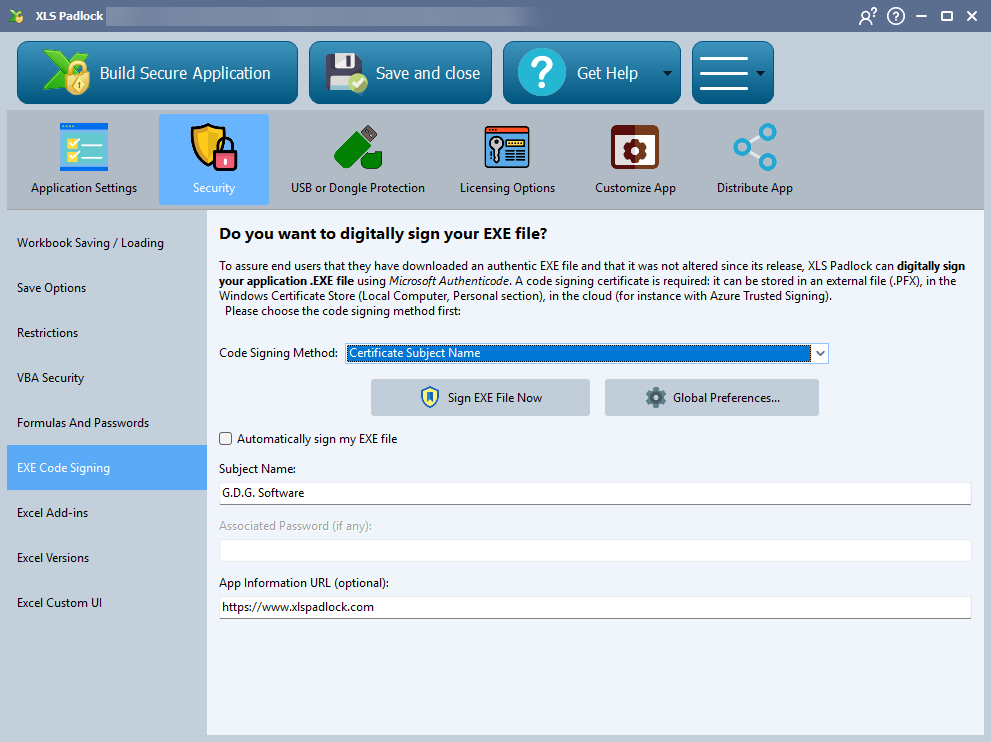
Configuring Code Signing in XLS Padlock #
In the XLS Padlock interface, navigate to the Security -> EXE Code Signing tab. To enable signing, choose your preferred Code Signing Method:
- PFX File: Uses a certificate stored in a
.pfxfile. This is a legacy method for older certificates. - Certificate Subject Name: Locates the certificate in the Windows Certificate Store by its Subject Name. This is a common method for certificates on hardware tokens.
- Certificate Thumbprint: Locates the certificate in the Windows Certificate Store by its unique Thumbprint (a SHA-1 hash). This is often the most reliable method.
- SignTool Commands: An advanced method that allows you to provide custom commands for Microsoft’s
SignTool.exeutility, offering maximum flexibility. Azure Trusted Signing: Signs your application with Microsoft’s cloud-based service. See our Azure Trusted Signing Tutorial for more details.
Azure CLI Required
To use this method, you must first install the Microsoft Azure CLI and log in using
az login.
Performing the Signing #
- Manual Signing: Click Sign EXE File Now to immediately sign the last built EXE file.
- Automatic Signing: Check Automatically sign my EXE file to have XLS Padlock sign the EXE every time you build your application.
Troubleshooting
If a signing error occurs, check the detailed messages in the XLS Padlock compilation log. This log file is typically named [Your Workbook Filename].xplcompil.log and is located in the same directory as your workbook.